Retailing and manufacturing are areas where human beings are the key players, and they need to act fast, stick to the procedure strictly, and be flexible in case of any trouble. It is difficult to scale up old-school teaching methods and extensive reading materials, while the learning process at the workplace could end up affecting either the efficiency or the safety negatively.
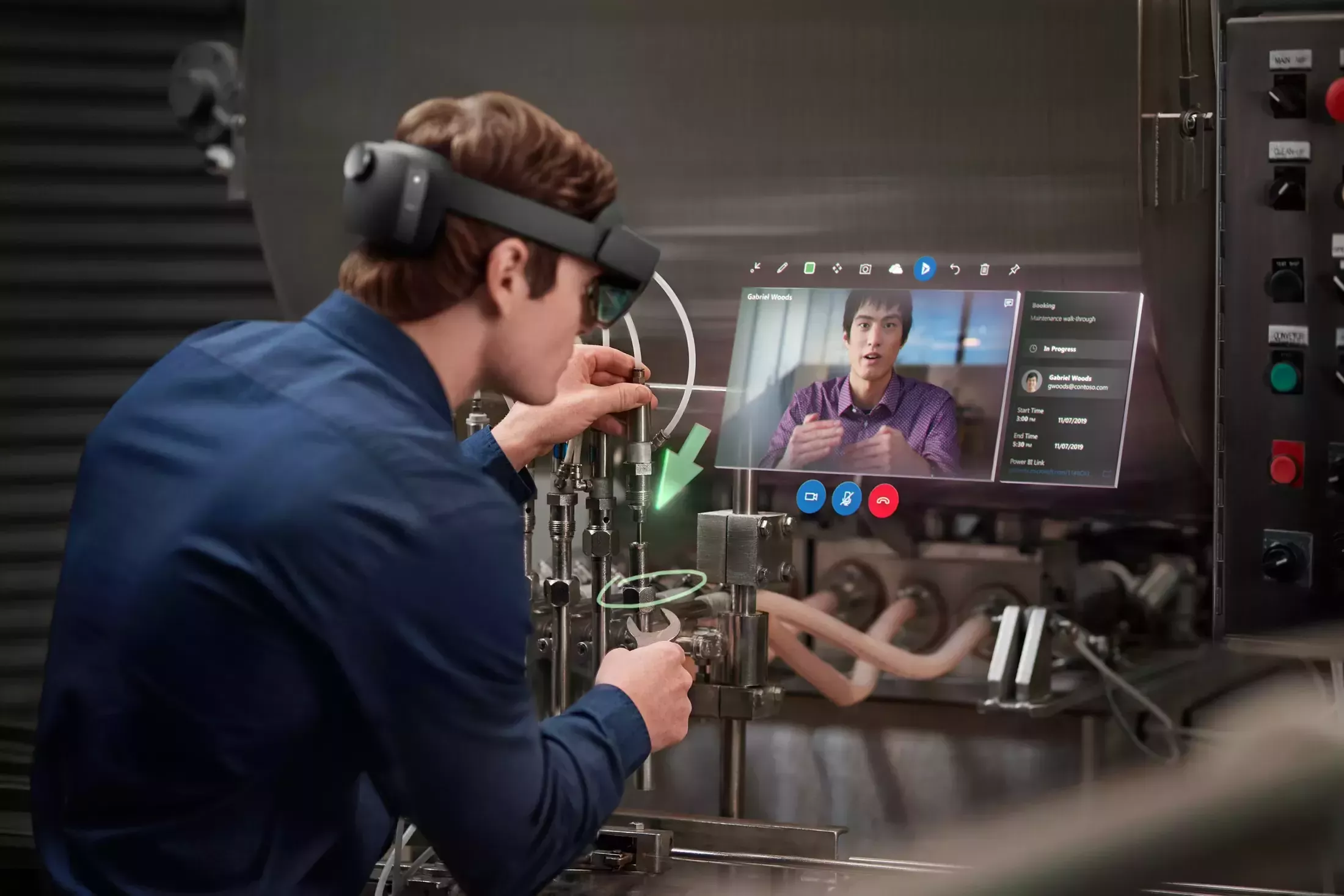
One of the most innovative methods for industry training has been the use of augmented reality along with three-dimensional replicas, which are commonly referred to as digital twin training. This enables employees to train within the actual environment, obtain real-time assistance as needed, and carry out the essential tasks repeatedly without affecting the workflow. In the following, I will describe the functioning of these tools, the major areas of their impact, and the ways by which companies can implement them.
Which Frontline Problems are Solved Best by Immersive Training?
Many training gaps arise from constraints that are common to retail and industrial settings.
- Limited time for hands-on practice, because rosters and production schedules leave little spare capacity.
- Retail staff turnover is high, and it demands fast onboarding that will not only be cost-effective but also will help maintain a reliable quality of service.
- Complex factory equipment or layouts where errors can lead to not only unsafe situations but also very expensive downtimes. Unsteady training, where results are determined by the trainer who is available during that particular week.
- Need to train on rarely occurring events, such as emergency shutdowns or peak period crowd control, which cannot be practiced safely on live operations.
AR workforce training and 3D twins address these by putting immersive, repeatable practice where the learner is and by converting tacit knowledge into visible, guided tasks.
How Do Augmented Reality Overlays and 3D Twins Deliver Practical Learning?
Three core capabilities make the approach effective.
1. Context-aware instruction:
AR overlays place step-by-step guidance directly on machines, shelves, or workstations. A new hire can see and handle positions, torque sequences, or product placement cues through smart glasses or a tablet, which shortens the path from instruction to correct action.
2. Spatially accurate rehearsal with a digital twin training model:
A 3D twin is no more than a digital replica of a physical asset, a production line, or a retail store layout. It allows the trainees to simulate the installation of equipment, evacuation procedures, and flows of replenishment in a virtual model that truly reflects their actual workplace. This reduces the cognitive gap between practice and performance.
3. Behavioral measurement and adaptive practice:
Sensors and software log actions, timing, and errors. Learning systems use that data to create personalized drills, focusing practice where the learner needs it most, for example, picking speed, machine changeover time, or correct shelf facings.
What Outcomes Should Retail and Factory Managers Expect?
Clear, measurable improvements follow when implementation is aligned to business goals.
- Faster onboarding, with new staff reaching core competency in fewer supervised shifts.
- Fewer operational errors, like misplaced stock, wrong assembly steps, or wrong lockout procedures, happened.
- Better safety for employees, as they can practice dangerous tasks in a virtual environment.
- Uniform customer experience in all shops because visual standards are being maintained through augmented reality checklists.
- Less line downtime, as technicians can perform maintenance steps and fault diagnosis on a 3D twin before working on the actual equipment.
These results are the most probable when the scenarios are about the tasks that bring the most rework, delay, or risk.
What Does Good Curriculum Design Look Like for Immersive Training?
Practical principles for educators and L&D teamsStart with the task and the error modes, not the tech. Translate a recurring mistake into a set of observable actions that can be guided and measured.
- Use short, repeatable modules so practice fits into shift patterns. Micro sessions of ten to twenty minutes work well for shop floor staff and retail associates.
- Blend modes combine AR-assisted practice, instructor-led review, and real-world guided shifts. The virtual session primes the learner; the on-site coach consolidates the behavior.
- Include multi-role team scenarios, particularly in retail for peak hour responses and in factories for coordinated maintenance or emergency drills. AR can synchronize cues across devices so teams rehearse communication and timing.
- Build meaningful assessments with objective metrics such as time to complete a task, error rate, and adherence to procedure.
Use those metrics for targeted refreshers.
Which Technologies and Integrations Matter Most?
Choose tools that fit operational constraints.
- Device flexibility, because not every site can support wearable headsets. Solutions should work with tablets, phones, and optional headsets.
- Offline capability, since factory networks or store connectivity can be intermittent. Local caching of 3D twins and AR overlays avoids training interruptions.
- Integration with workforce systems, so completion records, certifications, and refresher schedules flow into your learning management system.
- Easy authoring tools, enabling subject matter experts to create or tweak scenarios without depending on external vendors for every change.
- Data export and privacy controls to make sure performance logs are available for coaching while complying with local regulations.
How to Pilot and Scale Without Disrupting Operations
A stepped approach reduces risk and builds stakeholder confidence.
- Select a use case that has a great impact, such as a new employee store merchandising, an important maintenance process, or an emergency shutdown drill.
- Develop a minor storyline, perform a trial with a small group of people, and gather both numeric and non-numeric feedback.
- Show economic benefit by means of the reduction of time to competency, fewer errors, or faster maintenance cycles.
- Expand to other locations, adjusting for regional layout differences and language.
- Institutionalize the practice by training internal facilitators and embedding immersive sessions into regular refresh schedules.
What Challenges are Likely, and How to Manage Them?
Anticipate practical obstacles and responses.
- Resistance to new devices is overcome by starting on familiar hardware like smartphones and by showing quick wins.
- The content maintenance burden is reduced by investing in authoring tools and local content owners.
- Measurement noise is handled by correlating simulation metrics with real-world KPIs over time, not relying on one-off snapshots.
- Privacy and consent issues, addressed through transparent policies, anonymized performance data where possible, and clear use cases for coaching versus disciplinary action.
Conclusion
Applying augmented reality (AR) overlays and 3D twinning techniques in the immersive learning process can result in faster training, fewer repeated errors, and improved safety in both stores and manufacturing settings. The most valuable programs focus on specific, high-impact tasks, pair virtual practice with on-site coaching, and measure results with clear operational metrics.
If you want a partner to design and deliver AR workforce training, implement digital twin training, or explore AR training retail / industrial AR training at scale, Limina Studios in Dubai offers end-to-end services, including scenario design, 3D twin creation, and deployment support, helping teams move from pilot to repeatable value.