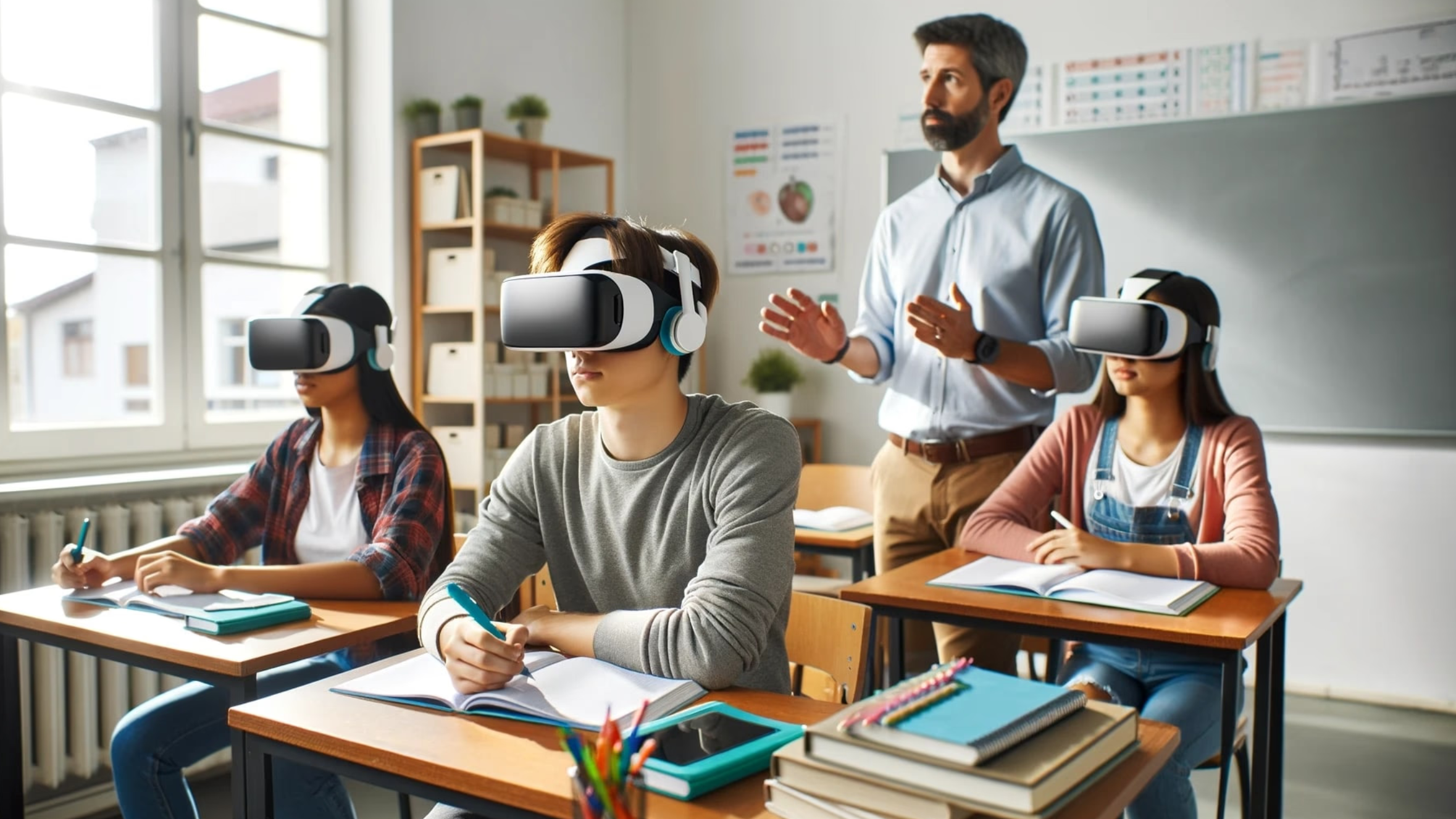
Training matters, whether the goal is to lower error rates on a production line, prepare medical staff for rare procedures, or onboard new retail employees. This post compares immersive methods against classroom and e-learning approaches, explains where each method excels, and helps learning designers choose the right mix for measurable results.
What are virtual reality training benefits for employees?
Virtual reality training benefits for employees go beyond novelty. Learners in a virtual environment carry out realistic tasks in a risk-free manner, repeating situations over and over until muscle memory is built up, and performance metrics are captured automatically with high detail by trainers.
VR is an environment that allows trainees to not just learn but also to make mistakes in the process of strengthening their correct responses while being subjected to controlled stressors that resemble real work situations for the roles where spatial judgement, procedural accuracy, or high-stakes decision-making are critical.
Key employee benefits include:
- Faster skill acquisition, because learners perform tasks instead of only reading or watching.
- Safe failure, because mistakes in VR do not cause physical harm or production losses.
- Higher learner engagement, because interactive practice beats passive consumption.
- Objective assessment, because systems log actions, timings, and error patterns for review.
These points explain why many service industries and manufacturing firms now include virtual reality training benefits for employees in their procurement briefs.
Comparing VR training vs traditional training outcomes
When you compare VR training vs. traditional training outcomes, the differences appear in three practical dimensions: time, depth, and recall.
- Time to competency: VR usually shortens it. Trainees that practice in situ learn routines faster than those who only study manuals or attend lectures.
- Depth of learning improves because VR forces procedural practice, and repeated simulation under varied conditions builds judgment, not just rote steps.
- Recall improves as well, because embodied learning, the kind that ties actions to outcomes, creates stronger memory traces than passive reading.
That said, traditional training keeps value where conceptual frameworks, policy discussion, or complex interpersonal skills are the target. Classroom settings still shine for debate, for transferring tacit cultural knowledge, and when learners require group coaching and peer feedback.
How immersive training for employees reduces on-the-job errors
Practical training that mimics the workplace reduces errors; here is how immersive training for employees contributes to operational safety and quality control.
First, trainees confront realistic hazards in a controlled setting, which builds threat recognition. Second, systems can randomize failure modes, which prepares staff for the unpredictable. Analytics first spot areas of weakness in the performance of every individual, and hence, trainers can prescribe targeted remediation. Moreover, the use of scenario replay allows teams to scrutinize their choices and improve their coordination without disrupting the ongoing operations.
This phenomenon illustrates how companies significantly reduced their incident rates after the introduction of well-conceived immersive programs.
Virtual reality training cost vs traditional training cost
Cost comparisons for virtual reality training cost vs. traditional involve direct and indirect expenses as well as the time factor.
Initially, VR incurs hardware, software development, and integration costs. On the other hand, traditional training involves expenses for classroom space, instructional materials, and instructor wages, along with the cost of productivity loss due to staff being removed from their work for training. However, over time, the per-learner cost of VR declines since content is reused for all cohorts and simulation-based refreshers replace recurring instructor time.
In the case of complex or high-risk skills, VR very often is the winner in the contest of total cost of ownership if the costs related to mistakes, accidents, and the time taken for new employees to get accustomed to the work are all reduced.
A practical approach to budgeting would be to project the total cost over three years, factor in the anticipated loss reductions due to errors, and give the cohorts that correspond to your organization a comparison of scenarios.
Designing blended programs that combine virtual reality training modules with existing methods
Most mature L&D teams adopt a blended model, where virtual reality training modules complement, not replace, other approaches. A typical pathway looks like this:
- Prework: short microlearning modules to establish vocabulary and objectives.
- VR module: immersive practice that emphasizes procedure and situational judgement.
- Facilitated debrief, a classroom or online meeting where performance data is reviewed and implications are discussed.
- In-field coaching, supervised application of skills with a mentor, to bridge simulation and reality.
This sequence preserves social learning, yields measurable practice time, and ensures that VR investments return operational value. Use VR for repetitive, spatial, and safety-related skills, and use human-led sessions for nuance, policy discussion, and cultural expectations.
Measuring success with virtual reality training metrics for companies
Good programs define metrics before deployment. Useful virtual reality training metrics for companies include:
- Time to competency, measured as days or hours until a trainee passes a practical assessment.
- Error rate reduction, tracked by incident reports pre- and post-training.
- Retention of skills at three and six months, using practical tests.
- Transfer rate: percentage of skills applied correctly on the job.
- Learner satisfaction and perceived confidence, collected through surveys.
Analytics inside VR make many of these metrics easy to capture, which turns training into a continuous improvement engine.
When virtual reality training for healthcare professionals makes sense
Healthcare benefits significantly from simulation because procedural accuracy and sterile technique matter. Virtual reality training for healthcare professionals is powerful for:
- Rare but critical procedures, where practice opportunities are limited.
- Team coordination in emergencies, where communication patterns matter.
- Patient interaction scenarios, when you want to rehearse difficult conversations in a low-risk setting.
- VR does not remove the need for cadaver labs or supervised clinical hours; however, it accelerates readiness so students and residents arrive at patient care better prepared.
Common pitfalls to avoid when implementing VR training for employees
Even the best technology fails if rollout is poor. Avoid these common mistakes when you adopt VR training for employees.
- First, do not treat VR as a single silver bullet; match it to the right skill sets.
- Second, ignore change management at your peril, because adoption depends on managers and supervisors endorsing practice time.
- Third, skip analytics at your own risk; without measurement, you cannot prove return on investment.
- Fourth, neglect accessibility, ensure comfort settings for motion sensitivity, and take into account learners with special needs.
A pilot program that defines success criteria, gathers feedback, and iterates is far more effective than a large, rushed deployment.
Practical checklist for choosing the best virtual reality training platforms for enterprise
If you are evaluating vendors, use this checklist for the best virtual reality training platforms for enterprise.
- Content fidelity: Does it model your tasks accurately?
- Reporting: Can you integrate data into your LMS or BI tools?
- Scalability: Can the platform serve multiple sites and large cohorts?
- Ease of authoring: Does the tool let internal teams adapt scenarios?
- Hardware support: Does it work with the devices you prefer? Support and service, vendor responsiveness for updates and troubleshooting.
Ask for a pilot project with a limited scope, not the whole range, and require measurable outcomes related to actual business metrics.
Future directions for virtual reality training trends for 2026 and beyond
It is quite difficult to accurately predict the features that the future will bring; nonetheless, these trends are quite reasonable to expect for virtual reality training trends for 2026 and beyond.
- Greater interoperability, wherein simulation data is such that the enterprise systems are perfectly informed.
- More user-friendly authoring tools, to the effect that even the subject matter experts are able to create scenarios without any programming.
- Lower-priced hardware, hence more access not only for big companies but also for small ones.
- More intelligent analytics, which are capable of relating training activities with performance at the end of the production line.
What counts foremost is practical, where training meets operational needs, and that measurement is the basis for continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Virtual reality and conventional training both have their advantages. VR is the best for hands-on repeat practice, making situational judgments, and learning safety-critical skills, while traditional methods are still the best for making concepts clear, facilitating group discussion, and introducing the organization’s culture.
The shortest route to superior 3D learning experiences and results is the adoption of the combination, the use of specific metrics, and the treatment of simulations as part of a larger learning ecosystem.
If your company wants real support for immersive training development and deployment, Limina Studios in Dubai provides virtual reality training solutions tailored to your needs. Our services include the creation of virtual reality training modules, 3D instructional assets, and integration with enterprise learning systems, making us a practical partner for teams that want to move from pilot to scale.