These days, virtual reality has transformed itself from being an imaginative yet distant dream into a groundbreaking technology with impacts across most sectors. VR is changing how we play, learn, heal, or transact real estate as we interact with the world around us. But what is virtual reality, and how does it manipulate today and tomorrow?
What is Virtual Reality?
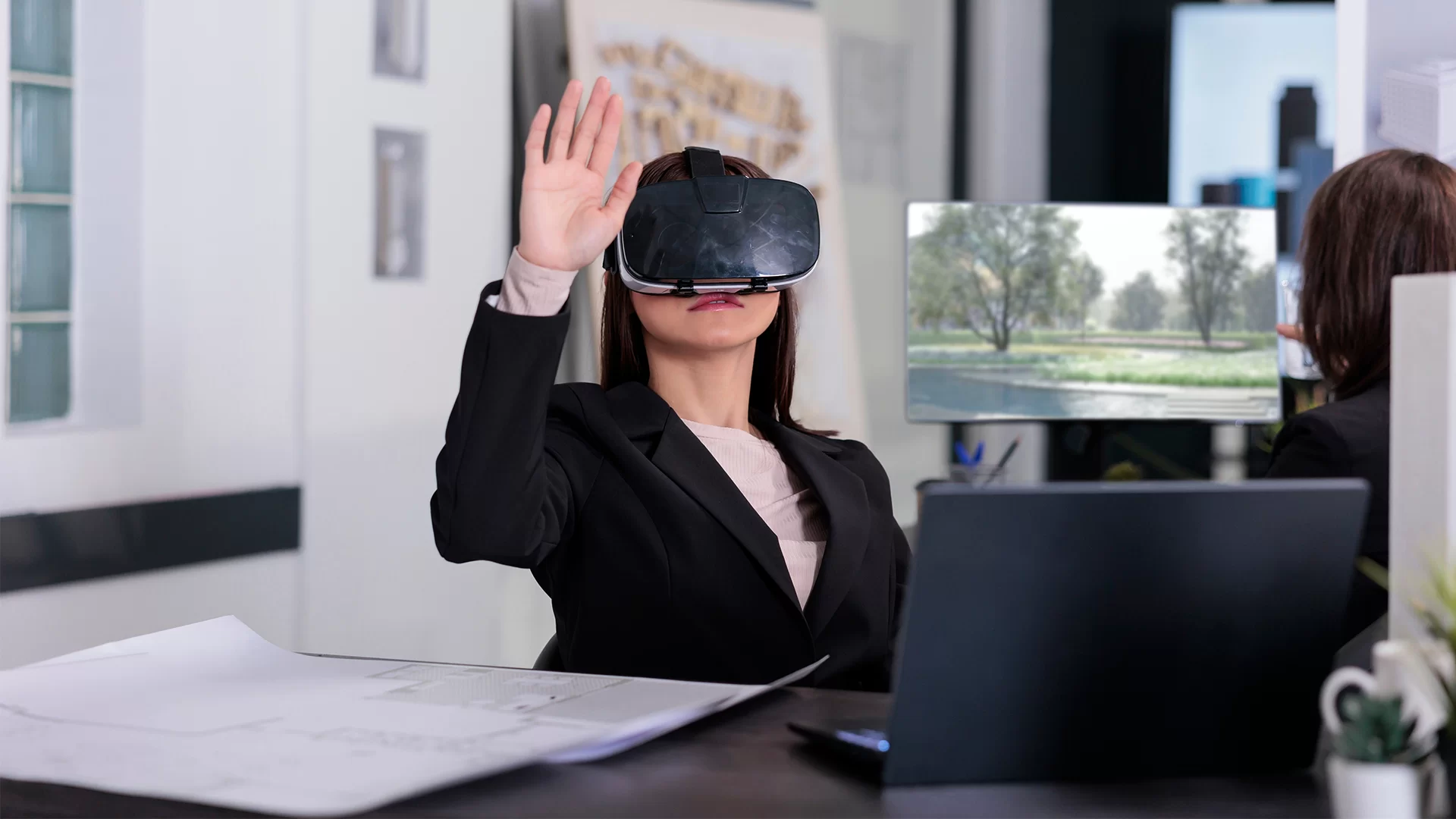
So, what is virtual reality? Quite simply, virtual reality is a computer-generated simulation that immerses users in an artificial environment and commonly involves wearing a head-mounted display or gloves and/or using motion controllers.
Unlike traditional screens, it tracks the head or body movement of the user so that his surroundings also move in accordance with his position and momentum as though he was really there inside the 3-dimensional world.
That is the premise of virtual reality to create as seamless an immersion as possible without it being tactile.
The Evolution of Virtual Reality
Although one may feel that VR should belong in recent times, it really dates back several decades. It’s as recent as the 1960s when the idea of voluptuous devices like the Sensorama, which gave way to a multisensory experience, made a mark on the early minds.
Development in the years to come would see increasing public acceptance of virtual reality—the natural outcome of increasing computing power and graphics. Most of the time, virtual reality can be associated with games in the 1990s, but poor technology did not allow it to reach a larger audience.
The 2010s began with companies like Oculus, HTC, and Sony opening the floodgates for affordable yet very good-quality VR headsets. Today, VR is becoming more accessible, ranging in usage from almost everything outside of entertainment.
Types of Virtual Reality
A full understanding of VR would entail looking into all the various types of virtual reality. These include:
1. Non-immersive VR
This is the entry-level form of virtual reality and concerns users operating with a basic screen, like a standard monitor or television. A prime example is simulation-based video games that permit users to control the avatars created within a virtual space.
2. Semi-immersive VR
Though providing an even richer experience than non-immersive, semi-immersive VR has yet to achieve the standard of complete immersion. At this level, projection systems or massive display surfaces give a sense of depth and presence. Classic examples are flight simulators used in training a pilot.
3. Fully Immersive VR
It is the most complete and most sophisticated kind of virtual reality, where an individual can use all possible modern tools like VR goggles and even motion-tracking equipment. The user completely penetrates the virtual cosmos with its 3D objects, which one can manipulate in real time. Popular examples of this immersive experience are virtual tours and VR gaming.
Applications of Virtual Reality
There are numerous and increasing applications of virtual reality transforming industrial function and audience engagement. Let’s take a glimpse at a few primary uses:
1. Gaming and Entertainment Gaming
is by far the most spearheaded ROI kind in all forms of application. Gaming via Oculus Rift and PlayStation VR takes players into its virtual suppression levels.
2. Education and Training
VR has brought up a brilliant new reality in education. All kinds of interactive learning environments have been created in history; for instance, students are virtually taken back in time, while in science, they perform experiments inside virtual labs.
3. HealthCare
Virtual reality (VR) can provide a means for surgical training, physical rehabilitation, and even treatment for mental health. For instance, patients suffering from anxiety or PTSD may receive exposure therapy through virtual means and expose themselves to their fears here in a regulated condition.
4. Real Estate and Architecture
Virtual reality is truly changing the industry’s landscape. Now, potential buyers are able to tour properties without leaving the comfort of their homes. It is likewise used by architects to virtually present to their clients 3D house designs.
5. Retail and E-commerce
These days, one can find retail organizations that employ virtual reality to augment the purchasing experience. With virtual fitting rooms, for instance, consumers can fit clothes virtually before buying, allaying concerns and reducing returns.
The Future of Virtual Reality
The evolution of virtuality is not showing any signs of stagnation, and as with technology, it is expected that VR will entice even more sensibility in the future with haptic suits for tactile feedback, lighter headsets for better comfort, and advances in AI for more realistic interaction.
Conclusion
No longer is virtual reality a futuristic fantasy; it is a transformative piece of reality woven into the very fabric of several industries, redefining and reshaping human experience. The understanding of virtual reality in what it entails and the various highly imaginative types available for one to relish will, hence, serve to appreciate the overall place of those experiences.
That’s how it’s done—watching movies or playing games, making arrangements for one’s educational development, or conducting the training process. All avenues through which VR is breaking barriers. If you’re interested in what virtual reality can do and want to put it to work in your business or creative projects, consider teaming up with Limina Studios, based in Dubai, they will build you a bespoke next-generation virtual reality experience that brings your ideas to life within a spectacular virtual setting.