Without proper guidelines, it is hard to navigate any indoor space. Indoor navigation systems resolve it in an efficient way. Systems like this use technology to make it easier for us all to navigate tricky indoor spaces. Be it a hospital, mall, or office, indoor navigation makes the user experience better. It will give accurate direction, and you will not feel lost. It is a good move if we look stressed out indoors.
In this article, we go over what indoor navigation systems are and how they work to show why they are in fact necessary.
What is Indoor Navigation and Why is It Important?
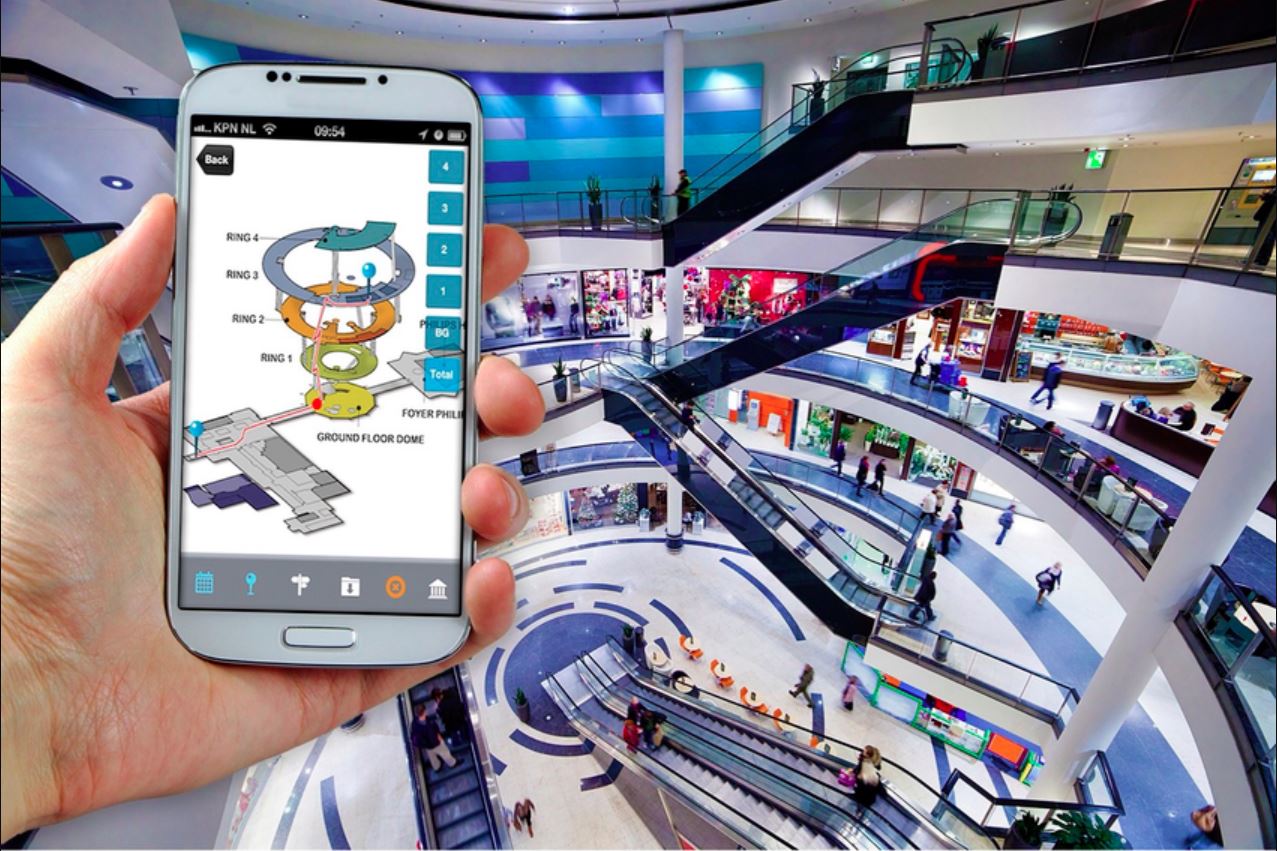
They are technologies used to assist people in navigating within buildings, referred to as indoor navigation. Indoor navigation systems are explicitly designed to operate within buildings, whereas GPS is meant for outdoor work. WiFi, Bluetooth, and sensors allow you to accurately locate the positions.
This technology is highly beneficial for hospitals, airports, shopping malls, etc. It helps visitors find their way to particular departments, stores, or gates. It helps increase user satisfaction overall and decrease frustration.
Businesses Improve security by following the movements with accurate indoor positioning. During emergency situations, fast navigation can make the difference between life and death. Modern infrastructure requires indoor navigation systems that provide convenience, and the most important one is safety.
How Do Indoor Navigation Systems Work?
Indoor navigation systems are complex networks that help users navigate through indoor venues. Indoor navigation, on the other hand, and outdoor navigation systems, which operate using GPS signals, require a mixture of technologies that integrate well with one another to achieve precision. So, here is how these systems work, and what are the key elements involved in indoor navigation that make it efficient and sustainable?

Specific technologies enabling indoor navigation
There are multiple technologies behind indoor navigation systems, each of which serves a different aspect in order to provide accurate positioning. Here are the primary ones:
Wi-Fi-Based Positioning
A Wi-Fi-based positioning system is one of the most widely used methods for indoor navigation. The system triangulates the user’s position by measuring signal strength from nearby Wi-Fi access points.
This is one of the most effective ways to accomplish this, but for places that have many Wi-Fi vendors, like shopping malls and airports, Because the precision of Wi-Fi positioning can be high, better than a few meters, it will perform well in many indoor environments.
Bluetooth Beacons
BLE beacons are small devices that emit signals to nearby smartphones or other devices. The beacons are strategically placed in a building to lay the foundation grid of beacon references. Each time a device hears beacons, it uses its strength and how far away it is from each of them to get an idea of where they are situated. Consequently, this technology is excellent for improving indoor navigation in environments such as museums and spacious retail stores.
IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units)
In terms of IMU, these are sensors used to measure acceleration and rotation information on a device. Most of the time, they are asserting with other techs for good positioning details. For example, the IMU can estimate movement and direction when Wi-Fi or Bluetooth signals are weak to keep guiding the user. For locations where those signal-based approaches might not suffice, like deep underground or heavily obstacle-laden areas, IMUs are a critical tool.
Lidar and UWB
LiDAR and UWB are both high-accuracy indoor positioning technologies. LiDAR, on the other hand, makes such details by transmitting laser beams to render a very precise 3D map. LiDAR uses lasers, whereas UWB employs ultrawide-range (radio waves with low power) access technology, which measures proximity range up to meter level. The use of these technologies is primarily in industrial settings or complicated environments.
The Role of Mapping and Localization
Whether a phone, robotic vacuum, or autonomous car, mapping the area provides an essential blueprint for navigating in any indoor space. Localization simply places the user within that map, merging them for real-time navigation.
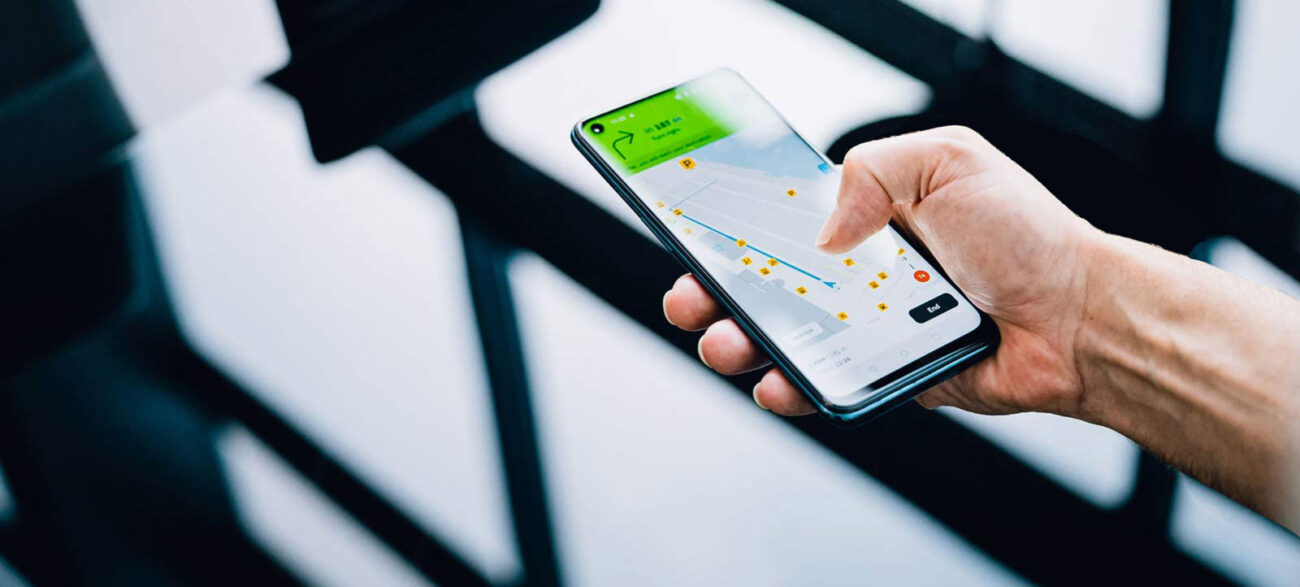

Indoor navigation systems revolve around digital maps enriched with floor plans and points of interest. Users are always on the move, and real-time positioning automatically adjusts their path, providing accurate directions. It provides the same dependable, easy-to-use experience as GPS but is designed for indoor use.
User Interaction and Experience
Indoor navigation apps typically focus on providing a smooth user experience. The majority of them are embedded into mobile apps that show maps, directions, and user feedback. Using simple visual and auditory cues, travelers can quickly input their destination and receive intuitive guidance.
What are essentially interfaces (mobile apps) to be abstracted as the primary means of searching for places, viewing maps, and getting directions in real-time? The apps usually also have add-ons like augmented reality (AR) for improved navigation as well. It is also with the help of any disabled or elderly users who may find this public transport difficult; otherwise, audio cues and routes suitable for wheelchairs are enforced to make it a completely inclusive system.
Conclusion:
Indoor navigation systems are transforming the way we navigate intricate indoor spaces. Such systems combine Wi-Fi technologies with Bluetooth beacons and digital mapping capabilities to give precise, real-time instructions. These make the user experience friendly, enhance security and are also for everyone. Indoor navigation is becoming a necessity, whether in the hospital or other places like malls and airports.
If you are in Dubai and want to apply this cutting-edge approach, contact Limina Studios. At Limina Studios, we specialize in indoor navigation systems to create human-focused spaces, helping all users easily and intuitively find their way around a facility.